When it comes to the processing of metals and metal powders, one process has increasingly become the centre of attention in recent years: 3D printing. In this article, we have therefore summarised for you what 3D printing can do and what advantages it offers for the metal industry.
3D printing: more than just a gimmick
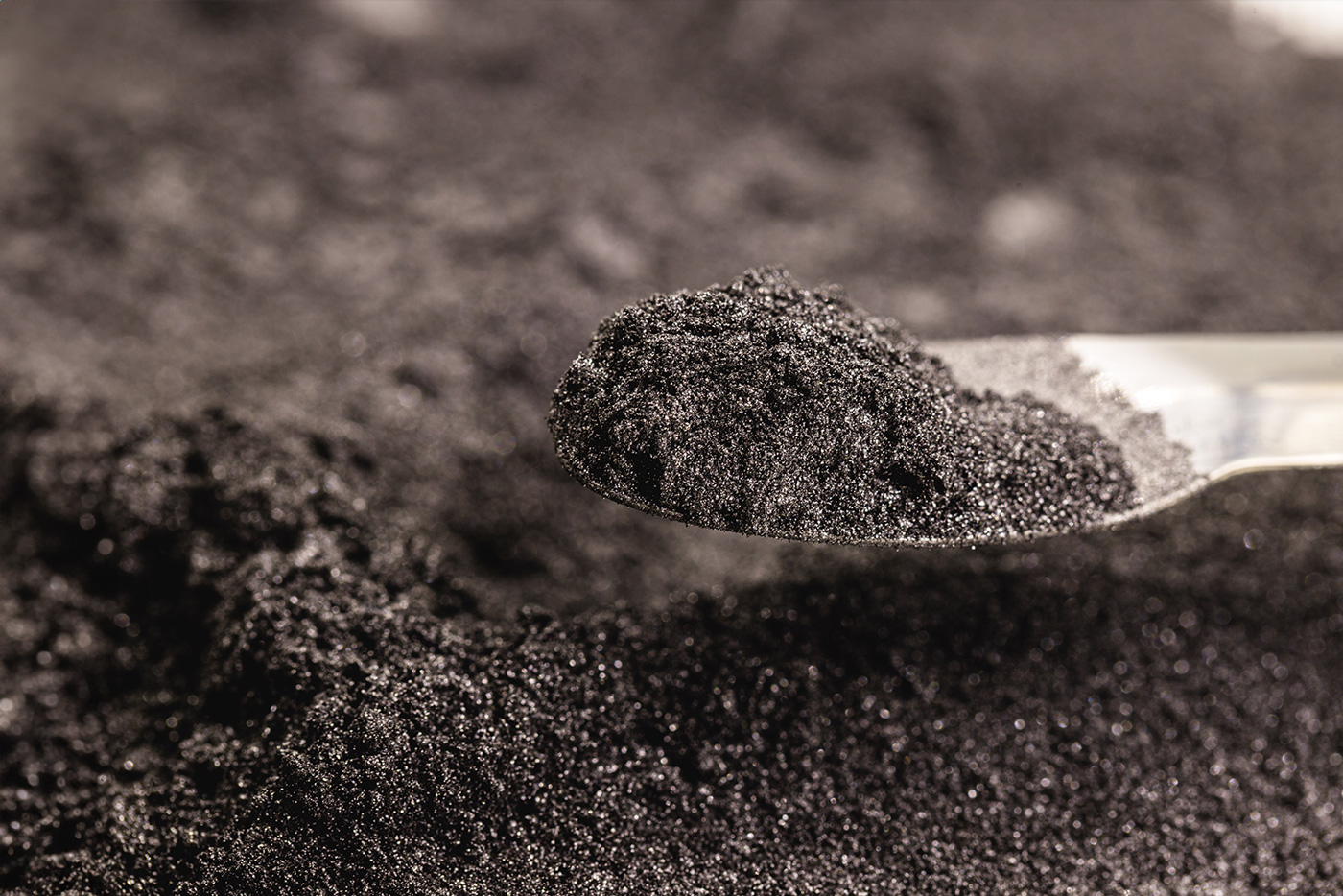
3D printing has long since ceased to be of interest only to ambitious hobbyists or experts keen to experiment. On the contrary: 3D printing is gradually establishing itself in more and more industries and areas of application, bringing with it new possibilities and innovations. While plastic initially played a major role in additive manufacturing, a wide range of materials are now available. Whether food, artificial joints or entire houses: the development of innovative applications is progressing.
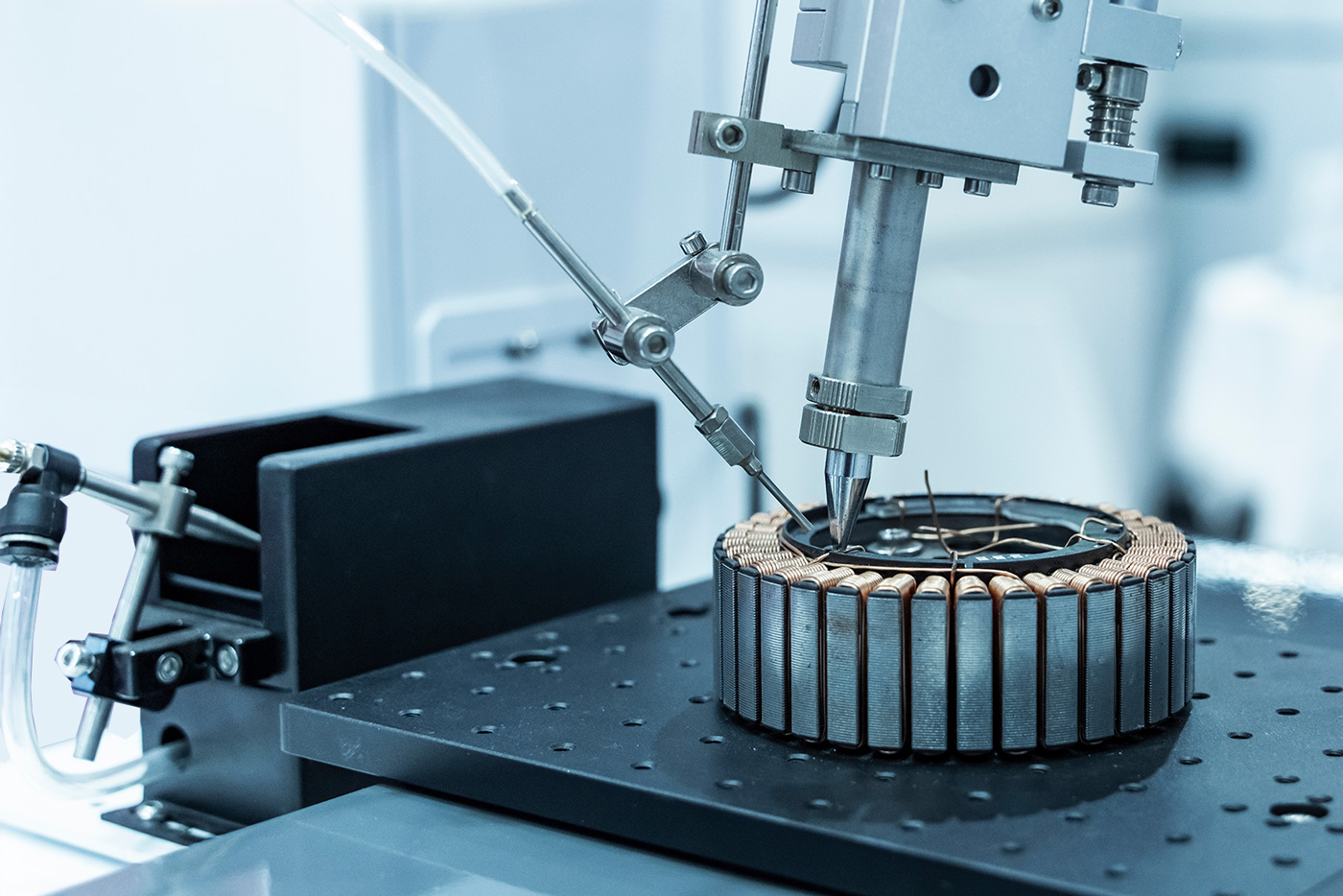
Less visionary, but already part of everyday life, is the 3D printing in the metal industry. Because even the most diverse metals can be moulded into the desired shape with the right 3D printer.
What are the advantages of additive manufacturing?
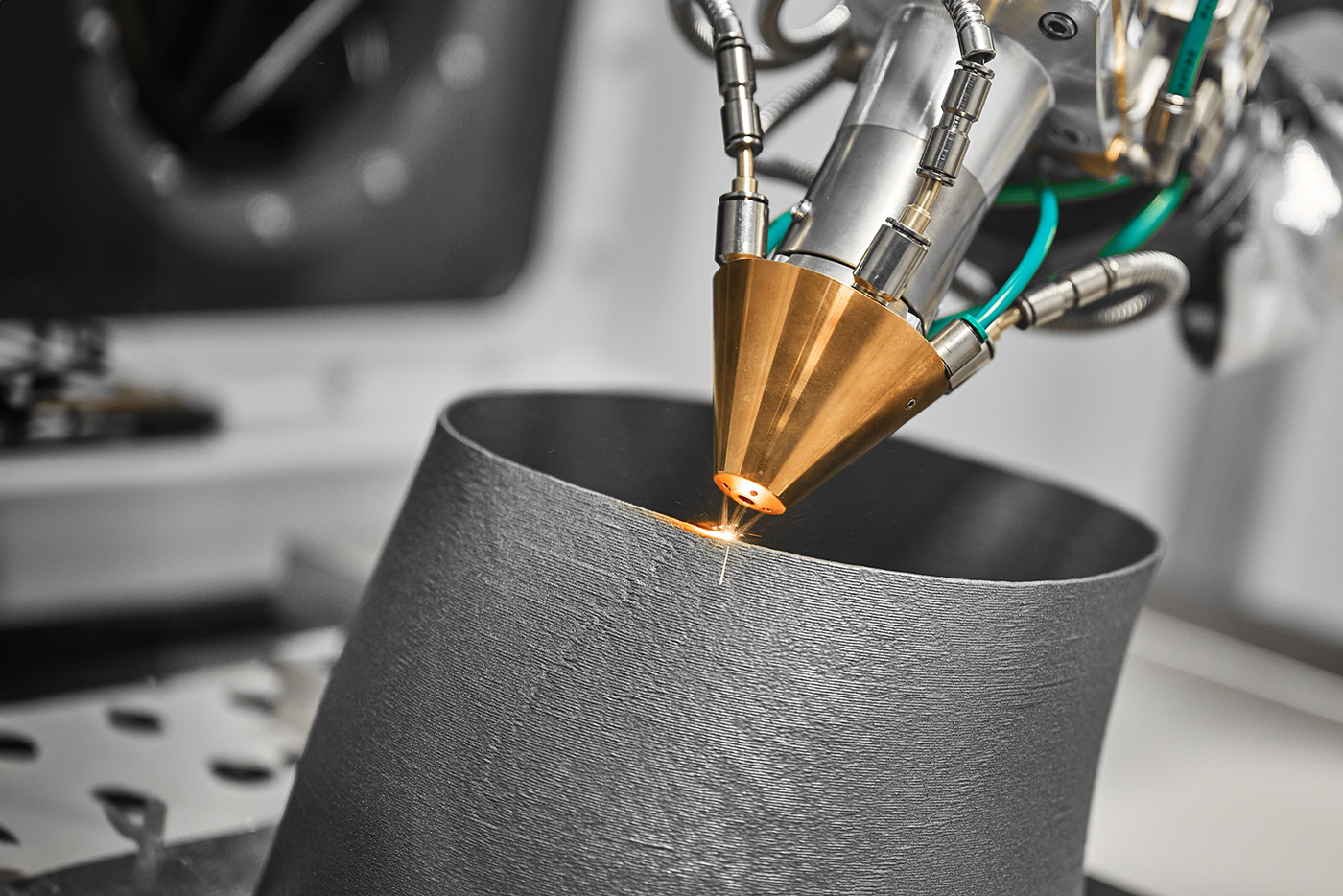
When the advantages of 3D printing are considered, it is always in comparison to traditional manufacturing processes such as injection moulding, sintering or the processing of solid materials. Good to know: 3D printing is not a single specific manufacturing process. In fact, there is a wide range of basic processes and permanent new developments such as laser melting or laser deposition processes that cover different areas of application. However, the main advantages of 3D printing are common to all processes.
High flexibility
3D printing is characterised by its high level of flexibility, among other things. Components can be produced quickly and spontaneously, meaning that no production in advance is necessary. High storage costs for unused workpieces are therefore eliminated. Customised adaptations of individual components can also be carried out more quickly and easily compared to traditional manufacturing processes. This allows you to react better to customer requests or changes.
3D prints require less post-processing
One of the strengths of 3D printing is its high precision. Deviations from the plan hardly ever occur. The technology gives you the opportunity to produce complicated components to the highest standard without the need for time-consuming post-processing. This saves you time and costs during production.
3D printing reduces maintenance costs
Additive manufacturing makes it possible to produce even complex components as if they were "cast from a single mould". Instead of several small, fragile components that have to be put together, you can produce a combined workpiece. This reduces the costs for maintenance and repairs - a price advantage that you can either pass on to your customers or use to maximise profits.
Generally speaking, it can be said: With the right 3D printer, valuable resources can be saved in production. The entire process is streamlined and offers simple options for customisation.
Where is 3D printing used in the metal industry?
Theoretically, 3D printing of metals can be used in all areas in which metal processing is also focussed in the traditional way. The main areas of processing are Nickel, Steel, Titaniumcopper, Aluminium, Magnesium in pure form or as an alloy, but also metals such as Stainless steel. Areas of application include, for example
- Automotive industry: Development of prototypes, production of components for the luxury segment, initial production of series parts
- Aerospace: Engines
- RailwaySpare parts
- Tool manufacture: Injection moulds
- Medical technologyProstheses, implants
Wherever complex geometries, small components, weight reduction or the minimisation of the number of components are required, 3D printing can score points - regardless of the industry.
3D printing in the metal industry: potential for today and tomorrow
The metal industry is already benefiting from 3D printing technology. Problems such as comparatively high costs for larger production volumes and the lack of universally applicable standards are some of the reasons why the full potential of this manufacturing process has not yet been realised. However, manufacturers of 3D technologies are rapidly developing their products, so that additive manufacturing in the metal industry continues to advance. Perhaps there is something for you too - whether today or tomorrow.