Titanium powder is used in additive manufacturing and numerous areas of powder metallurgy. However, the fine metal powder is not entirely harmless. In this article, we show you the challenges that arise and how to deal with them.
Titanium powder: metal powder with special features
Titanium powder is one of the most popular metal powders in various areas. For example, its high compatibility makes it a frequently used material when it comes to implants for the human body. However, titanium and titanium alloys are also frequently used for jewellery or in the aerospace industry. After all, the metal is characterised by its low density and therefore minimal weight. However, the processing of titanium powder requires a certain amount of caution.
General hazards in powder metallurgy
In general, working with metal powders poses a particular risk to the lungs and mucous membranes. Depending on the element, inhaling metal dust can cause mild to severe health problems. In addition to these typical challenges when working with metal powder, which can normally be easily overcome with the right protective equipment, titanium powder poses a further risk.
Titanium powder: reactive and risky
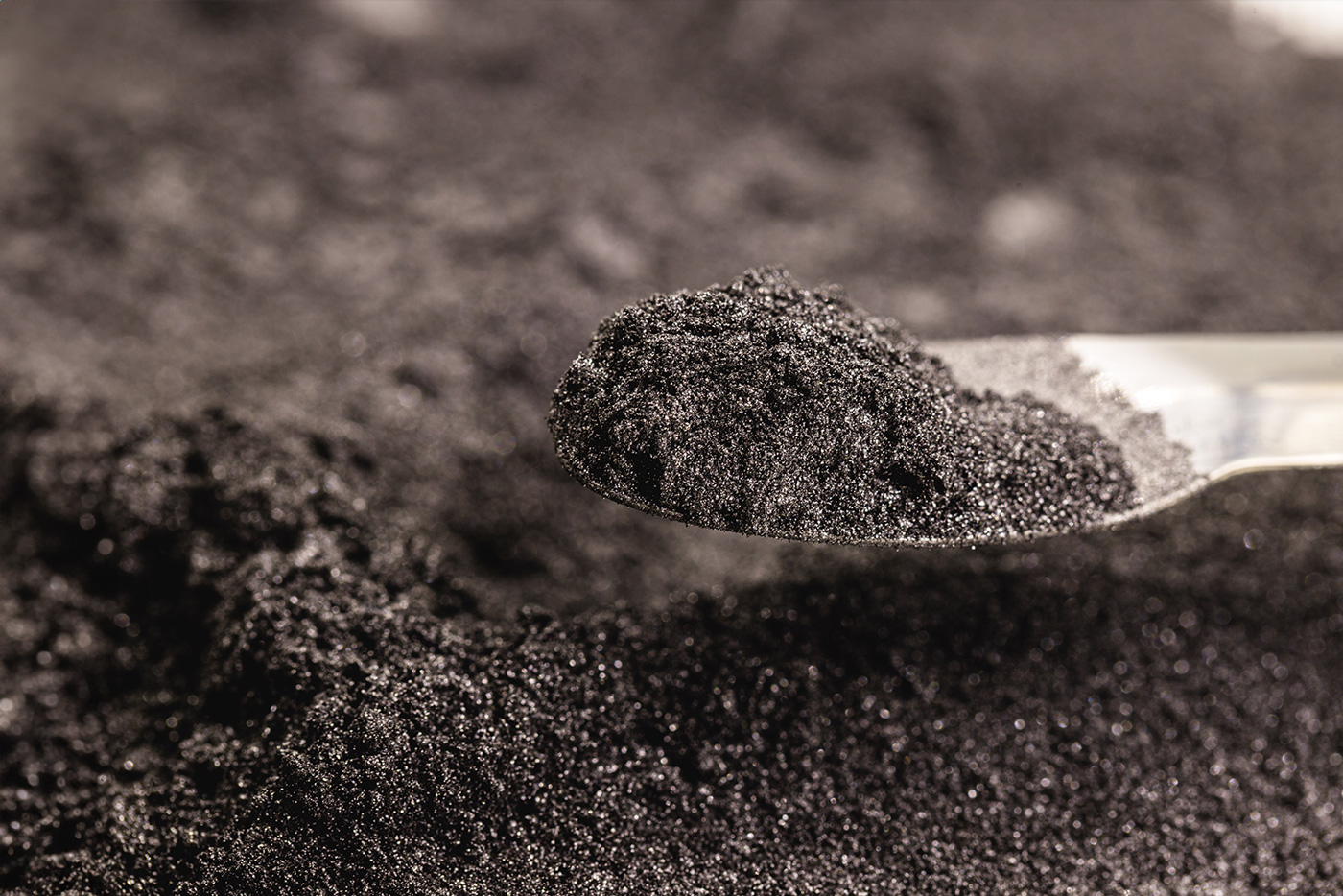
In compact form, titanium is completely harmless - in powder form, however, there is a high risk of fire. Light metal powders such as titanium, but also magnesium or aluminium, are extremely flammable to the point of spontaneous combustion. The flammability depends on factors such as the grain size. In general, the finer the titanium powder is distributed, the greater the risk.
The swirled up titanium dust reacts with the room air even at room temperature. The resulting heat of reaction ultimately leads to spontaneous combustion. Powder residues that settle on work clothing can even cause clothing to burn. A single spark, for example from a grinder, is sometimes enough to trigger this.
Tips for the correct handling of titanium powder
However, the dangers that titanium powder can pose are no reason to avoid this high-performance material. If you get the basics right when handling titanium powder, you can minimise risks and benefit from the advantages.
Tip 1: Safe storage
Titanium powder must be stored tightly sealed and kept away from sources of heat and ignition. The recommended storage temperature can normally be found in the manufacturer's instructions. The containers and the equipment to be filled must be earthed. The storage location itself should be dry and well ventilated and fulfil the legal requirements of a safety storage facility for flammable hazardous substances.
Tip 2: Practised handling
Some precautionary measures can and must also be taken at the processing site to ensure the safe handling of titanium powder. The room should be well ventilated, lighting and ventilation systems are explosion-proof. Handling under inert inert gas minimises contact with the air.
Anyone working with titanium powder must wear appropriate protective clothing. This includes safety goggles, gloves, flame-retardant protective clothing for the body and respiratory protection. Contaminated clothing is changed before changing workplaces, at the end of the working day or before the break to prevent the aforementioned clothing burn.
Tip 3: Prepare for an emergency
If, despite all precautions, a light metal fire involving titanium powder occurs, it must never be extinguished with water. Light metals react strongly with water. The resulting hydrogen is also highly flammable and, in the worst case, can lead to an explosion. Extinguishing agents containing water, such as foam, are therefore also not suitable for extinguishing a titanium fire. Special extinguishing agents or extinguishing equipment must therefore be available at the processing and storage site. Suitable extinguishing agents include metal fire powder, dry sand or noble gases such as argon.
Safety should not be compromised when handling titanium powder
When working with titanium powder, it is essential to comply with the relevant regulations and laws in order to protect the lives of employees. Among other things, the following should be taken as a basis:
- Hazardous Substances Ordinance
- Industrial Safety Ordinance
- TRGS 800 "Fire protection measures"
- DGUV-R 113-001 "Explosion protection rules"
You should familiarise yourself thoroughly with the regulations before use. If the applicable rules are observed, the risk of spontaneous combustion or other accidents with titanium powder is minimised as far as possible. However, the greater effort required compared to less dangerous metal powders pays off in the long term thanks to the special properties of titanium.