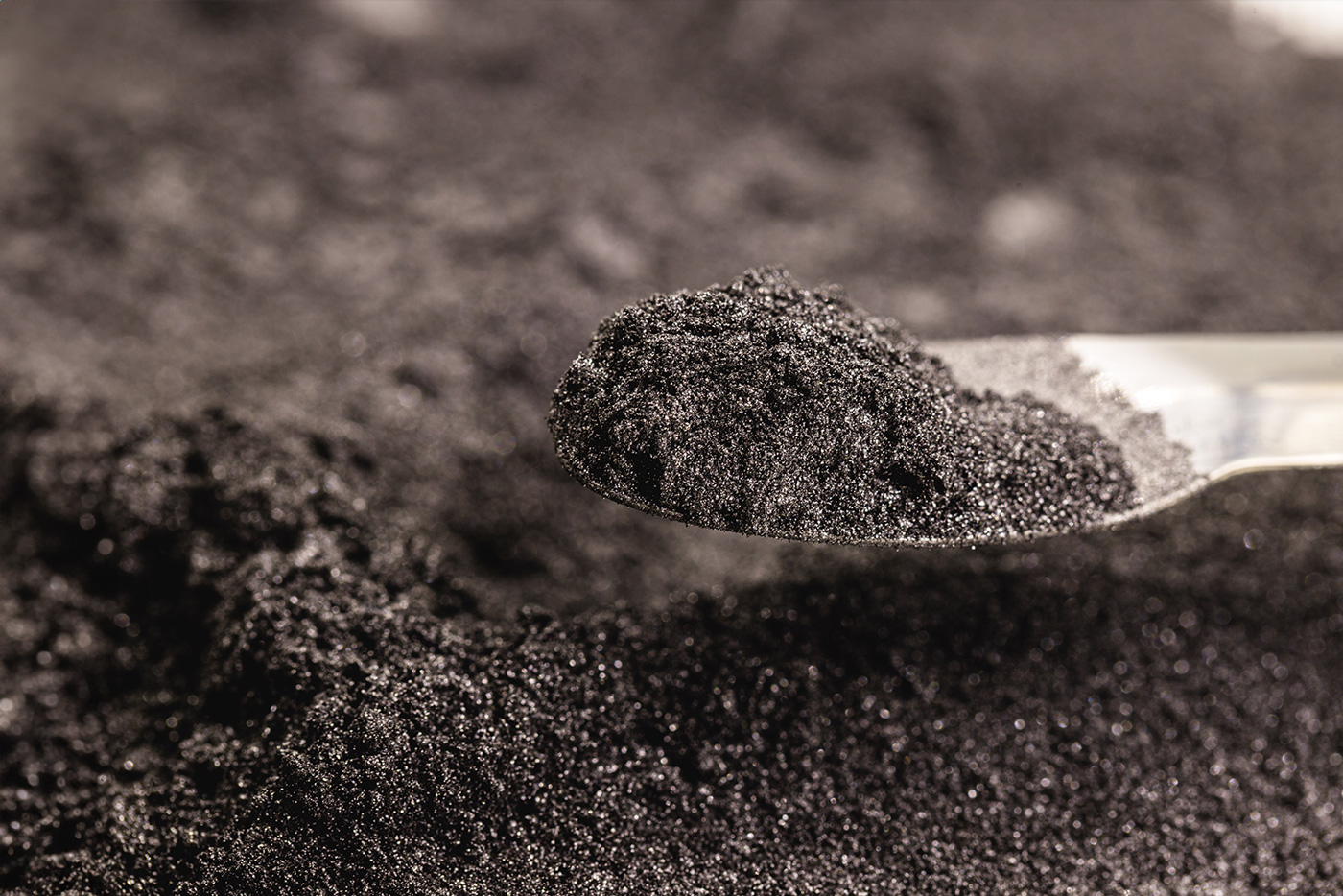
Aluminium powder plays a role in powder metallurgy and other branches of industry that should not be underestimated. But what are the advantages of using the metal powder and what problems can arise during processing? We'll tell you in the following article.
Application in the industry
Whether as aluminium foil, in the form of a folding garden chair or as a particularly lightweight component in the automotive industry: aluminium is omnipresent in everyday life as well as in industry. Aluminium is not only used as a solid material. Above all Aluminium powder is used in numerous application areas and industries:
- Additive manufacturing
- Paints and varnishes
- Catalyst in chemistry
- Drug production
- Cosmetics production
- Explosives and fireworks
- Production of alloys for mechanical engineering and vehicle construction
Advantages of aluminium powder
The wide range of applications for aluminium powder is no coincidence. The fine particles have certain advantages with which they can score points across all industries.
Advantage 1: Improved material properties
Pure aluminium is rarely used due to its comparatively high cost. Instead, the substance is used to upgrade other materials. If aluminium powder is used as an additive in casting or pressing, for example, this can lead to an improvement in certain material properties. Specifically, this mainly involves
- Impact strength
- Compressive strength
- Thermal conductivity
- Corrosion resistance
- UV resistance
- Food-safe
- Low weight
Aluminium can improve the performance of highly stressed components in particular, some of which are exposed to adverse conditions. In the form of alloys, the positive properties can be easily transferred to the desired workpieces.
Advantage 2: Recycling to aluminium powder enables cost-effective and sustainable alternatives
Aluminium is the third most common element in the earth's crust. However, it is not found in its pure form and therefore requires a lot of energy and time to extract, which in turn entails high costs. The pure light metal is correspondingly expensive and does not have a particularly good reputation when it comes to environmental protection.
On the other hand, the more resource-efficient and significantly cheaper Recycling aluminium - and in particular the production of so-called secondary powders. Recycled aluminium powders obtained from remnants can therefore be an attractive alternative to working with the solid material or other light metal powders in terms of profitability and sustainability. The European recycling rate for aluminium is already just under 70%. Compared to primary production, 95% of energy can be saved through recycling.
Disadvantages of aluminium powder
In addition to the aspects of energy consumption and costs, the dangers during processing must be considered when using aluminium powder. Ultra-fine aluminium dust reacts easily with oxygen even at room temperature, so appropriate safety measures must be taken in the factory and staff must be professionally trained. Various sources of danger are relevant here:
- Aluminium powder is combustible and flammable.
- If aluminium powder mixes with the air, dust explosions can result.
- Contact with water, acids or alkalis can produce highly flammable hydrogen.
- Reactions with oxidising agents such as nitrates or sulphates can also cause fire and explosion hazards
- The electrostatic charge can cause electrical discharges that can lead to the ignition of a cloud of aluminium dust.
To minimise these dangers and prevent accidents and injuries, it is essential that rooms and personnel are properly stored and equipped. Much of this also applies to the handling of other metal powders such as titanium, so that no major changes are possible when changing or adding aluminium powder. The measures and regulations include
For storage
- Conductive, earthed packaging
- Store in a dry place
- Store in a cool place
- Store separately from incompatible substances and liquids
For the premises and equipment
- High level of cleanliness to avoid the accumulation of dust
- Avoid potential sources of ignition (open fire, hot surfaces, etc.)
- Natural or technical ventilation
- Inertisation options to interrupt the oxygen supply in an emergency
For the employees
- Respiratory protection
- Hand protection
- Head and face protection: helmet with heat and flame protection grille
- Workwear made of flame-retardant special fabric, with dissipative finish
- Foot protection in the form of dissipative safety shoes
For all parts of the protective equipment, compliance with the corresponding DIN standards to ensure maximum protection.
The star among light metal powders
Aluminium powder continues to be popular due to its many exciting properties, regardless of sector or industry. And with the possibilities of additive manufacturing even more ideas and innovations can be realised with the powder. If your company already has experience in handling metal powders and has established appropriate safety standards, you should not shy away from aluminium powder and exploit the material's potential.